What is whole grain?
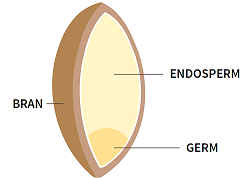
Whole grain in its natural state growing in the fields represents the entire seed of a plant. This seed is also called a “kernel” and consists from three edible parts (bran, endosperm and germ).
Bran
Bran represents the multi-layer outer skin of the edible kernel. Bran contains important B vitamins, antioxidants and dietary fiber.
Endosperm
Endosperm represents largest portion of the kernel and it provides the food supply of the germ, which means that it provides essential energy to the young plant, so it can send roots down for water and nutrients, and send sprouts up for sunlight’s photosynthesizing power. Endosperm contains proteins, carbohydrates and small amounts of vitamins and minerals.
Germ
Germ is the embryo which can sprout into a new plant and it contains B vitamins, proteins and minerals [1].

The most common whole grains are: whole wheat, brown rice, whole grain barley, whole rye, whole grain cornmeal, buckwheat and oatmeal [2].
Nutritional value of whole grains
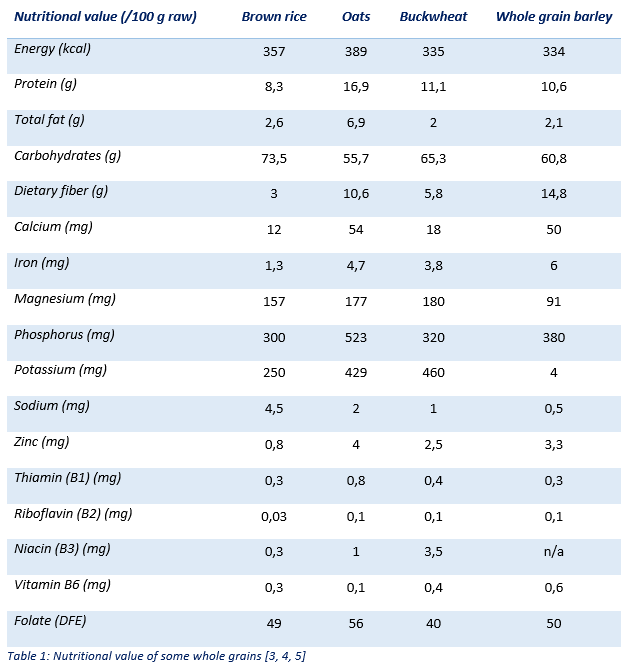
Grains constitute a major source of carbohydrate, protein and dietary fiber [1]. They also contain B vitamins, minerals (magnesium, zinc, iron and phosphorus) and other bioactive compounds (antioxidants) [2]. In the table below there are presented the nutritional values for some whole grains (brown rice, oats, buckwheat and whole grain barley).
References:
1. The Whole Grains Council official website.
2. AACC International (2012b) American Association of Cereal Chemists, Whole Grains from a Mechanistic View.
3. USDA NNDB, U.S. Department of Agriculture, National Nutrient Database for Standard Reference.
4 . Dutch Food composition data (2016).
5. Norwegian Food Composition table (2012).